Thromboxane A2 (TX-A2) is a member of the eicosanoid family, produced from arachidonic acid via the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway. Activated platelets produce this potent lipid compound. It acts as a potent vasoconstrictor and boosts platelet aggregation. So, they play a major role in hemostasis and thrombosis.
TX-A2 breaks down very quickly in the body and turns into a more stable substance called Thromboxane B2 (TXB2). Since TXB2 lasts longer, it is usually measured to indirectly find out how much TX-A2 is being made.
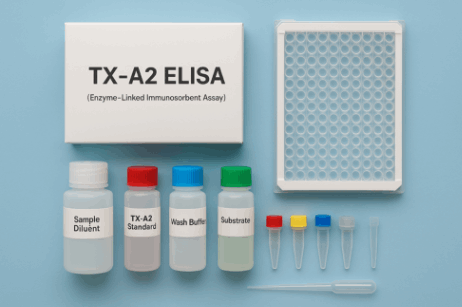
Researchers use TX-A2 ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kits to measure the level of TX-A2.
So, Why Measure TX-A2?
TX-A2 acts as a biomarker. Detection and quantification of TX-A2 is important, especially for research related to:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Thrombosis
- Inflammation
- Stroke
- Atherosclerosis
- Platelet dysfunction
- Kidney disease
This also helps study disease mechanisms, identify drug efficacy, and monitor physiological responses. For instance, high TX-A2 level implies high platelet activation, which can further lead to cardiovascular diseases.
What is TX-A2 ELISA?
TX-A2 ELISA is a highly sensitive immunoassay technique used to detect and quantify native thromboxane A2 levels in a sample, such as serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, and cell culture supernatants.
ELISA is conducted in 4 formats: direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive. However, TX-A2 ELISA uses a competitive binding format. In this, the TX-A2 in a sample competes with a labeled TX-A2 HRP conjugate for antibody binding sites.
Components of the TX-A2 ELISA kit are:
- Pre-coated microwell strip plates – These plates are pre-coated with TX-B2 or a specific antibody to ensure consistent results.
- Sample diluent and assay buffers – These help prepare and maintain the right conditions for the reactions.
- TX-A2 Standards – Known concentrations of TXB2 are used to generate a standard curve for quantification.
- Enzyme Conjugate (HRP-labeled TX-A2) – Thromboxane A2 conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP), used to create a measurable signal.
- HRP substrate detection system – Typically, a chromogenic substrate like TMB (tetramethylbenzidine), which changes color upon reacting with HRP.
- Stop solution – Stops the enzymatic reaction to lock in the signal.
- Wash solution – Removes unbound reagents from the wells to reduce background signal.
How Does TX-A2 ELISA Work?
The TX-A2 ELISA is based on a competitive binding format, which operates on the principle that free (unlabeled) TX-A2 in the sample will compete with enzyme-labeled TX-A2 for a limited number of antibody binding sites. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the assay process:
1. Coating Phase
Although the microplates come pre-coated, it’s important to understand that these plates are usually coated with TX-B2 or a specific antibody that binds TX-B2. This step provides a fixed target for binding during the competition phase.
2. Competitive Binding
During the assay, the biological sample (containing unknown amounts of TX-B2) is added to the wells, along with a known amount of HRP-labeled TX-B2. These two forms of TX-B2—one from the sample and the other conjugated with HRP—compete for the limited antibody binding sites present in the well.
3. Washing Step
Once the competitive binding interaction has occurred, any unbound material is thoroughly washed away using the provided wash solution. This ensures that only the antibody-bound complex remains in the well.
4. Detection Step
Next, a chromogenic substrate (often TMB) is added to the wells. This substrate reacts with the HRP enzyme, producing a color change, typically from colorless to blue.
5. Stopping the Reaction
After a fixed incubation period, a stop solution is added. This typically turns the blue color to yellow and halts the enzymatic reaction.
6. Quantification
The final color intensity is measured using a microplate reader (spectrophotometer) at a specific wavelength, often 450 nm. Importantly, in a competitive ELISA, the amount of color developed is inversely proportional to the concentration of TX-B2 in the sample. This means:
- More TX-B2 in the sample → Less HRP-TXB2 binding → Weaker color signal
- Less TX-B2 in the sample → More HRP-TXB2 binding → Stronger color signal
A standard curve generated using known TX-B2 concentrations allows researchers to interpolate the TX-B2 levels in unknown samples.
The Bottom Line
The TX-B2 ELISA kit has become an indispensable tool for scientists and researchers investigating the role of thromboxane A2 in health and disease. By measuring TX-B2 via an ELISA kit, researchers can get valuable insights into platelet function, inflammation, and more.
If you need TX-B2 ELISA kits for your research projects, make sure you get them from a reliable supplier.